SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.351 Variant, Beta)

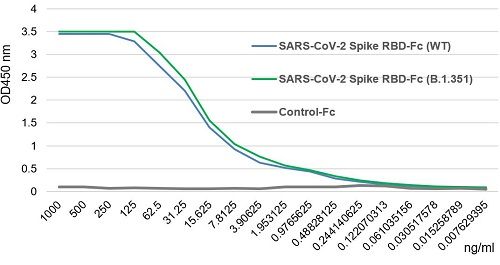
Figure 1: SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (B.1.351 Variant, Beta) binds to the receptor ACE2 (human) (rec.) slightly stronger than SARS-CoV-2 Spike Protein S1 (RBD):Fc (human) (rec.) (WT)
Roll over image to zoom in
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 50 µg |
| Purification : | 95% (SDS-PAGE) |
| Content : | 1mg/ml after reconstitution. Reconstitute with 50µl endotoxin-free water. Formulation: Lyophilized. Contains PBS. |
| Storage condition : | Short Term Storage +4°C Long Term Storage -20°C |
| AA sequence : | Receptor-binding domain (RBD) of SARS-CoV-2 Spike protein S1 (aa 319-541) containing the mutations K417N, E484K, N501Y is fused to the N-terminus of the Fc region of human IgG1. |
| Uniprot ID : | QHD43416.1 |
| Alternative Name : | 2019-nCoV Spike Protein S1 (RBD); Spike Receptor Binding Domain Variant South Africa; 501Y.V2 |
Biological Activity: Binds to human ACE2. MW: ~60kDa (SDS-PAGE) Endotoxin Content: 0.01EU/μg purified protein (LAL test).
SARS-CoV-2 shares 79.5% sequence identity with SARS-CoV and is 96.2% identical at the genome level to the bat coronavirus BatCoV RaTG133, suggesting it had originated in bats. The coronaviral genome encodes four major structural proteins: the Spike (S) protein, Nucleocapsid (N) protein, Membrane/Matrix (M) protein and the Envelope (E) protein. The SARS Envelope (E) protein contains a short palindromic transmembrane helical hairpin that seems to deform lipid bilayers, which may explain its role in viral budding and virion envelope morphogenesis. The SARS Membrane/Matrix (M) protein is one of the major structural viral proteins. It is an integral membrane protein involved in the budding of the viral particles and interacts with SARS Spike (S) protein and the Nucleocapsid (N) protein. The N protein contains two domains, both of them bind the virus RNA genome via different mechanisms. The CoV Spike (S) protein assembles as trimer and plays the most important role in viral attachment, fusion and entry. It is composed of a short intracellular tail, a transmembrane anchor and a large ectodomain that consists of a receptor binding S1 subunit (RBD domain) and a membrane-fusing S2 subunit. The S1 subunit contains a receptor binding domain (RBD), which binds to the cell surface receptor angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) present at the surface of epithelial cells. Recently, a new variant of SARS-CoV-2, called B.1.351 (Beta), was detected in South Africa. This variant carries three mutations in the RBD at the positions 417, 484 and 501 (K417N, E484K, N501Y) and is associated with a higher viral load, which may suggest potential for increased transmissibility.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
|
There are currently no product reviews
|













.png)









