Anti-Caldesmon(smooth) Monoclonal Antibody (Clone: hHCD)

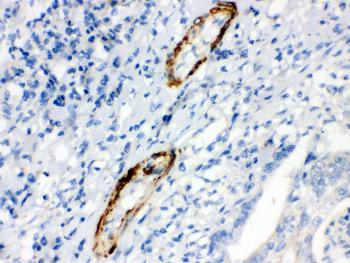
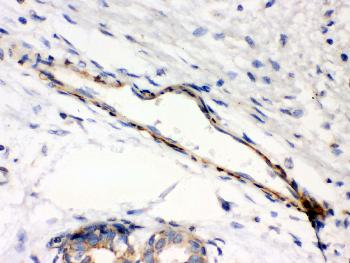
Figure 1: Anti-Caldesmon(smooth) antibody(39-1008). IHC(P): Human Intestinal Cancer Tissue.
Roll over image to zoom in
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 100 μg/vial |
| Isotype : | Mouse IgG1 |
| Purification : | Ascites |
| Content : | Each vial contains 50% glycerol, 1.2% Sodium acetate, 1% BSA, 0.02% NaN3. |
| Storage condition : | At -20˚C for one year, at 4˚C for one month. Avoid repeated freezing and thawing. |
Caldesmon is a potential actomyosin regulatory protein found in smooth muscle and nonmuscle cells. The predicted smooth-muscle polypeptide is 793 amino acids long. The high molecular weight caldesmon(h-CaD) is predominantly expressed in smooth muscles, whereas the low molecular weight caldesmon(l-CaD) is widely distributed in nonmuscle tissues and cells. Hayashi et al.(1992) demonstrated that the human CDM gene is composed of 14 exons.
Western blot : 0.25-0.5μg/ml; Immunohistochemistry(Paraffin-embedded Section) : 0.5-1μg/ml
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
| Subcellular location: | Cytoplasm, Cytoplasm |
| Post transnational modification: | In non-muscle cells, phosphorylation by CDK1 during mitosis causes caldesmon to dissociate from microfilaments. Phosphorylation reduces caldesmon binding to actin, myosin, and calmodulin as well as its inhibition of actomyosin ATPase activity. Phosphorylation also occurs in both quiescent and dividing smooth muscle cells with similar effects on the interaction with actin and calmodulin and on microfilaments reorganization. CDK1-mediated phosphorylation promotes Schwann cell migration during peripheral nerve regeneration. |
| Tissue Specificity: | High-molecular-weight caldesmon (h-caldesmon) is predominantly expressed in smooth muscles, whereas low-molecular-weight caldesmon (l-caldesmon) is widely distributed in non-muscle tissues and cells. Not expressed in skeletal muscle or heart. |
|
There are currently no product reviews
|













.png)










