Human N-Cadherin / CD325 / CDH2 Recombinant Protein (ECD, His Tag)(Discontinued)

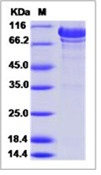
Fig 1: Human N-Cadherin / CD325 / CDH2 Recombinant Protein (ECD, His Tag)
Roll over image to zoom in
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 200 µg |
| Purification : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Content : | Formulation Lyophilized from sterile 20 mM Tris, 500 mM NaCl, 10 % glycerol, pH 7.4. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Storage condition : | Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| AA sequence : | Met1-Ala724 |
| Alternative Name : | CD325 Protein, CDHN Protein, CDw325 Protein, NCAD Protein, |
Source : Baculovirus-Insect Cells
Cadherins are calcium dependent cell adhesion proteins, and they preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells. Cadherin 2 (CDH2), also known as N-Cadherin (neuronal) (NCAD), is a single-pass tranmembrane protein and a cadherin containing 5 cadherin domains. N-Cadherin displays a ubiquitous expression pattern but with different expression levels between endocrine cell types. CDH2 (NCAD) has been shown to play an essential role in normal neuronal development, which is implicated in an array of processes including neuronal differentiation and migration, and axon growth and fasciculation. In addition, N-Cadherin expression was upregulated in human HSC during activation in culture, and function or expression blocking of N-Cadherin promoted apoptosis. During apoptosis, N-Cadherin was cleaved into 2-1 kDa fragments. It may provide a novel target for therapies that are directed toward intimal proliferative disorders, including restenosis and vascular bypass graft failure. N-Cadherin is associated with tumor aggressiveness and metastatic potential and may contribute to tumor progression.
Cadherins are calcium dependent cell adhesion proteins, and they preferentially interact with themselves in a homophilic manner in connecting cells. Cadherin 2 (CDH2), also known as N-Cadherin (neuronal) (NCAD), is a single-pass tranmembrane protein and a cadherin containing 5 cadherin domains. N-Cadherin displays a ubiquitous expression pattern but with different expression levels between endocrine cell types. CDH2 (NCAD) has been shown to play an essential role in normal neuronal development, which is implicated in an array of processes including neuronal differentiation and migration, and axon growth and fasciculation. In addition, N-Cadherin expression was upregulated in human HSC during activation in culture, and function or expression blocking of N-Cadherin promoted apoptosis. During apoptosis, N-Cadherin was cleaved into 2-1 kDa fragments. It may provide a novel target for therapies that are directed toward intimal proliferative disorders, including restenosis and vascular bypass graft failure. N-Cadherin is associated with tumor aggressiveness and metastatic potential and may contribute to tumor progression.
Endotoxin :< 1.0 EU per µg protein as determined by the LAL method.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
|
There are currently no product reviews
|














.png)










