Human FGF4 Recombinant Protein(Discontinued)
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 100 µg |
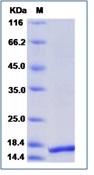
| Purification : | > 90 % as determined by SDS-PAGE. |
| Content : | Formulation Lyophilized from sterile PBS, pH 8.0. Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Storage condition : | Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| AA sequence : | Ser54-Leu206 |
| Alternative Name : | HBGF-4 Protein, HST Protein, HST-1 Protein, HSTF1 Protein, K-FGF Protein, KFGF Protein, |
Source : E. coli
FGF (fibroblast growth factor) signalling is known to be required for many aspects of mesoderm formation and patterning during Xenopus development and has been implicated in regulating genes required for the specification of both blood and skeletal muscle lineages. Fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) signaling induces differentiation from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) via the phosphorylation of downstream molecules such as mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase (MEK) and extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 (FGF-4) could not only increase the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), but also induce BMSCs into hepatocyte-like cells in vitro. FGF4 transduced BMSCs contributed to liver regeneration might by the transplanted microenvironment. The FGF4-bFGF BMSCs thus can enhance the survival of the transplanted cells, diminish myocardial fibrosis, promote myocardial angiogenesis, and improve cardiac functions.
FGF (fibroblast growth factor) signalling is known to be required for many aspects of mesoderm formation and patterning during Xenopus development and has been implicated in regulating genes required for the specification of both blood and skeletal muscle lineages. Fibroblast growth factor 4 (FGF4) signaling induces differentiation from embryonic stem cells (ESCs) via the phosphorylation of downstream molecules such as mitogen-activated protein kinase/extracellular signal-related kinase (MEK) and extracellular signal-related kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2). Fibroblast Growth Factor 4 (FGF-4) could not only increase the proliferation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs), but also induce BMSCs into hepatocyte-like cells in vitro. FGF4 transduced BMSCs contributed to liver regeneration might by the transplanted microenvironment. The FGF4-bFGF BMSCs thus can enhance the survival of the transplanted cells, diminish myocardial fibrosis, promote myocardial angiogenesis, and improve cardiac functions.
|
There are currently no product reviews
|













.png)










