Human FGF10 / KGF2 Recombinant Protein(Discontinued)
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 50 µg |
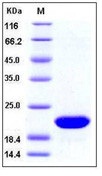
| Purification : | > 98 % as determined by SDS-PAGE |
| Content : | Formulation Lyophilized from sterile 20mM Tris, pH 7.5 Normally 5 % - 8 % trehalose, mannitol and 0.01% Tween80 are added as protectants before lyophilization. |
| Storage condition : | Store it under sterile conditions at -20°C to -80°C. It is recommended that the protein be aliquoted for optimal storage. Avoid repeated freeze-thaw cycles. |
| AA sequence : | Gln38-Ser208 |
| Alternative Name : | KGF2 Protein, |
Source : E. coli
Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF1 exhibits mitogenic activity for keratinizing epidermal cells, but essentially no activity for fibroblasts, which is similar to the biological activity of FGF7. FGF1 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. FGF1 is required for normal branching morphogenesis. It may play a role in wound healing. Defects in FGF1 are the cause of autosomal dominant aplasia of lacrimal and salivary glands (ALSG). ALSG has variable expressivity, and affected individuals may have aplasia or hypoplasia of the lacrimal, parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands and absence of the lacrimal puncta. The disorder is characterized by irritable eyes, recurrent eye infections, epiphora (constant tearing) and xerostomia (dryness of the mouth), which increases the risk of dental erosion, dental caries, periodontal disease and oral infections.
Fibroblast growth factor 1 (FGF1) is a member of the fibroblast growth factor (FGF) family. FGF family members possess broad mitogenic and cell survival activities, and are involved in a variety of biological processes, including embryonic development, cell growth, morphogenesis, tissue repair, tumor growth and invasion. FGF1 exhibits mitogenic activity for keratinizing epidermal cells, but essentially no activity for fibroblasts, which is similar to the biological activity of FGF7. FGF1 plays an important role in the regulation of embryonic development, cell proliferation and cell differentiation. FGF1 is required for normal branching morphogenesis. It may play a role in wound healing. Defects in FGF1 are the cause of autosomal dominant aplasia of lacrimal and salivary glands (ALSG). ALSG has variable expressivity, and affected individuals may have aplasia or hypoplasia of the lacrimal, parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands and absence of the lacrimal puncta. The disorder is characterized by irritable eyes, recurrent eye infections, epiphora (constant tearing) and xerostomia (dryness of the mouth), which increases the risk of dental erosion, dental caries, periodontal disease and oral infections.
Measured by its binding ability in a functional ELISA. Immobilized humen FGF10 at 10 µg/ml (100 µL/well) can bind Cynomolgus FGFR1-Fc with a linear range of 31.25-2000 ng/mL.
Other pack size also available.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
|
There are currently no product reviews
|














.png)









