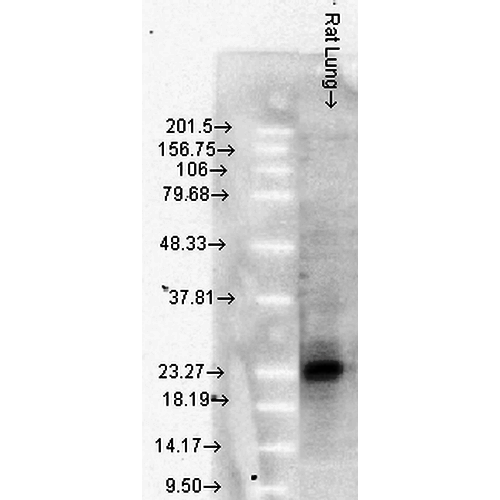
Anti-HSP27 Monoclonal Antibody (Clone : 8A7) - Alkaline Phosphatase(Discontinued)

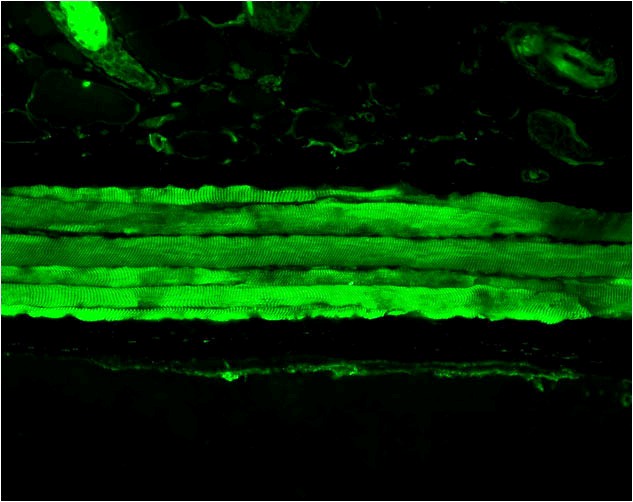
Figure1 : Mouse Anti-Hsp27 Antibody [8A7] used in Immunohistochemistry (IHC) on Rat embryo somites
Roll over image to zoom in
Shipping Info:
For estimated delivery dates, please contact us at [email protected]
| Amount : | 100 µg |
| Isotype : | Mouse IgG1 Kappa |
| Purification : | Protein G Purified |
| Content : | PBS, 50% glycerol, 0.09% sodium azide |
| Storage condition : | Store the antibody at 4°C |
HSP25 is the mouse homologue of the human HSP27 protein, a member of the small heat shock protein family comprised of a diverse group of proteins from ~15 to >30kDa(1). The basic structure of most sHSPs is a homologous and highly conserved amino acid sequence, with an alpha-crystallin-domain at the C-terminus and the WD/EPF domain at the less conserved N-terminus. This N-terminus is essential for the development of high molecular oligomers. HSP27-oligomers consist of stable dimers formed by as many as 8-40 HSP27 protein monomers. The oligomerization status is connected with the chaperone activity: aggregates of large oligomers have high chaperone activity, whereas dimers have no chaperone activity. HSP27 is localized to the cytoplasm of unstressed cells but can redistribute to the nucleus in response to stress, where it may function to stabilize DNA and/or the nuclear membrane. It can be rapidly phosphorylated in response to physiological stimuli relevant to the cell type examined. Thus, HSP27 has been suggested to be an important intermediate in second messenger-mediated signaling pathways. Other functions include chaperone activity (as mentioned above), thermo-tolerance in vivo, inhibition of apoptosis, and signal transduction.
Specifically, in vitro, it acts as an ATP-independent chaperone by inhibiting protein aggregation and by stabilizing partially denatured proteins, which ensures refolding of the HSP70 complex. HSP27 is also involved in the apoptotic signaling pathway because it interferes with the activation of cytochrome c/Apaf-1/dATP complex, thereby inhibiting the activation of procaspase-9. It is also hypothesized that HSP27 may serve some role in cross-bridge formation between actin and myosin. And finally, HSP27 is also thought to be involved in the process of cell differentiation. The up-regulation of HSP27 correlates with the rate of phosphorylation and with an increase of large oligomers. It is possible that HSP27 may play a crucial role in termination of growth.
WB (1:5000), ICC/IF (1:200), IHC (1:100); optimal dilutions for assays should be determined by the user.
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic/therapeutics procedures.
| Subcellular location: | Cytoplasm, Nucleus, Cytoplasm |
| Post transnational modification: | Phosphorylated upon exposure to protein kinase C activators and heat shock (PubMed:8325890). Phosphorylation by MAPKAPK2 and MAPKAPK3 in response to stress dissociates HSPB1 from large small heat-shock protein (sHsps) oligomers and impairs its chaperone activity and ability to protect against oxidative stress effectively. Phosphorylation by MAPKAPK5 in response to PKA stimulation induces F-actin rearrangement (PubMed:1332886, PubMed:8093612, PubMed:19166925). |
| Tissue Specificity: | Detected in all tissues tested: skeletal muscle, heart, aorta, large intestine, small intestine, stomach, esophagus, bladder, adrenal gland, thyroid, pancreas, testis, adipose tissue, kidney, liver, spleen, cerebral cortex, blood serum and cerebrospinal fluid. Highest levels are found in the heart and in tissues composed of striated and smooth muscle. |
| BioGrid: | 109547. 439 interactions. |
|
There are currently no product reviews
|
























.png)











